US News
NASA’s Voyager 2 probe reaches interstellar space
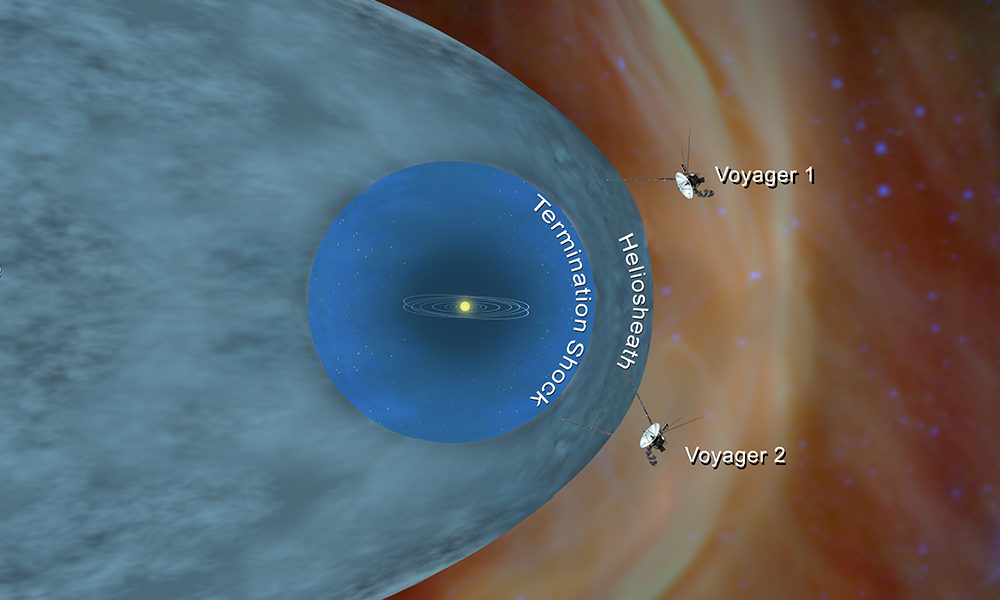
NASA’s Voyager 2 probe has entered interstellar space, becoming the second man-made object to reach the edge of the solar system, the U.S. space agency announced on Monday after a 41-year-long journey.
Data from the spacecraft shows that Voyager 2 crossed the outer edge of the heliosphere on November 5, NASA said. This boundary is where the tenuous, hot solar wind meets the cold, dense interstellar medium.
Voyager 2 is now more than 11 billion miles (18 billion kilometers) from Earth. Data sent by the spacecraft moves at the speed of light and takes about 16.5 hours to reach scientists back on Earth.
Its twin, Voyager 1, entered interstellar space in August 2012, but Voyager 2 carries a working instrument that will provide the first-ever observations from this gateway into interstellar space.
While the probes have left the heliosphere, they have not left the solar system, which extends until the outer edge of the Oort Cloud. It would take 30,000 years for Voyager 2 to leave the solar system.
The probes were launched 16 days apart in 1977 and both flew by Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2, which also flew by Uranus and Neptune, was built to last only 5 years and is now the longest continuously operating spacecraft in deep space.

-
 World1 day ago
World1 day agoU.S. and China report 3 more human cases of bird flu, UN calls for urgent action
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoU.S. Rep. Sheila Jackson Lee dead at 74
-

 Legal7 days ago
Legal7 days agoFlorida man arrested for threatening to kill Trump and Vance
-
 World1 week ago
World1 week ago7.4-magnitude earthquake hits northern Chile
-
 Legal5 days ago
Legal5 days agoAt least 19 people shot, 3 killed, outside Mississippi nightclub
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCyanide found on tea cups after 6 people die at Bangkok hotel
-

 Legal7 days ago
Legal7 days agoTexas Amber Alert: 2 children last seen in Bastrop County
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoKansas Amber Alert: Jaxon Halley abducted in Kansas City