Health
Uganda confirms fatal Ebola case in Kampala
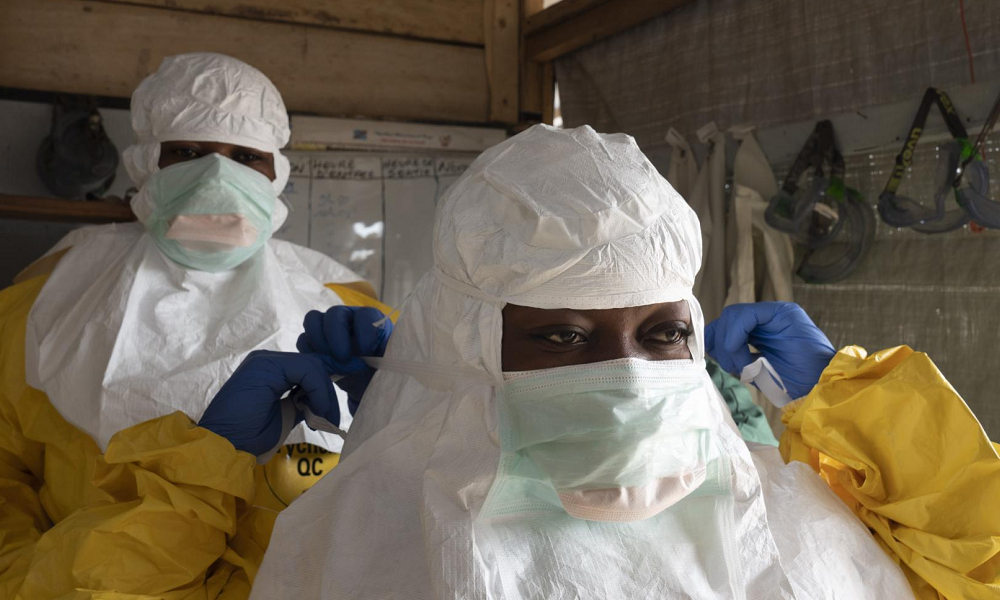

Uganda has confirmed a case of Ebola virus in its capital, Kampala, according to health officials. The patient died after seeking treatment at multiple facilities.
The case was confirmed by Uganda’s Health Ministry on Thursday. The patient, a 32-year-old male nurse employed at Mulago National Referral Hospital in Kampala, initially developed fever-like symptoms and sought treatment at several health facilities and from a traditional healer.
The patient presented with a five-day history of high fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing, which later progressed to bleeding from multiple body sites, according to the ministry. He experienced multi-organ failure and died at Mulago Hospital on Wednesday. Post-mortem samples confirmed Sudan Ebola Virus Disease (EVD).
A total of 45 contacts, including health workers, patients, and family members, have been identified and are currently under close monitoring, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Vaccination of all identified contacts against EVD is set to begin soon.
There have been eight previous outbreaks of the Sudan Ebola virus, with five occurring in Uganda and three in Sudan, according to WHO. Uganda last reported an outbreak of EVD in 2022.
“Banking on the existing expertise, we are accelerating all efforts, including expertise, resources, and tools to save lives and bring the outbreak to a halt swiftly,” said Dr. Kasonde Mwinga, a WHO Representative in Uganda.
Sudan Ebola virus disease is a severe, often fatal illness affecting humans and other primates. It is caused by Orthoebolavirus sudanense (Sudan virus), a viral species belonging to the same genus as the virus that causes Ebola virus disease. Case fatality rates for Sudan virus disease have ranged from 41% to 100% in past outbreaks.
The last outbreak in Uganda, in 2022, resulted in 77 deaths out of 164 cases across nine districts. In Kampala, there were 19 reported cases, including three deaths, according to a post-evaluation study published in The Lancet.

-

 Legal3 days ago
Legal3 days agoMichigan man JD Vance sentenced to 2 years for threatening Trump and JD Vance
-

 Politics4 days ago
Politics4 days agoU.S. to designate Maduro-linked Cartel de los Soles as terrorist organization
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoU.S. begins Operation Southern Spear against “narco-terrorists” in the Western Hemisphere
-
 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoCambodia reports fatal H5N1 bird flu case in 22-year-old man
-

 Legal1 day ago
Legal1 day agoWoman in critical condition after being set on fire on Chicago train
-
 World1 day ago
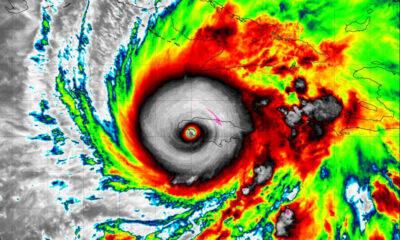
World1 day agoHurricane Melissa registered 252 mph wind gust, breaking global record
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoImprovised explosive device detonates outside Las Vegas restaurant; no injuries
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoNationwide power outage hits Dominican Republic



