Reviews
10 Best Strategies for Preserving Assets Before Medicaid

For people who need long-term care but want to preserve their assets before they qualify for Medicaid. Planning not only ensures that your loved ones continue to be financially secure but also have access to the necessary services they need. Awareness of differing strategies facilitates informed decision-making and the protection of valuable resources. This guide explores strategies for protecting assets before applying for Medicaid benefits.
1. Gifting Assets
An approach often used is giving assets in your estate to family members or close, trusted individuals. This strategy for preserving assets is effective, but it must be timed correctly without incurring a penalty. Medicaid has a five-year look-back period when transfers of assets will be examined. By planning, you will be compliant with regulations while also helping to safeguard your resources from being counted against you.
2. Establishing Trusts
One other useful tactic is the establishment of an irrevocable trust. This is achieved by transferring assets to a trust where the individual does not own the assets, but family members who benefit from the trust still receive benefits. Not all trusts are created equal when it comes to complying with Medicaid rules and regulations.
3. Purchasing Annuities
Annuities can also convert assets into an income stream, which can be helpful. For this reason, Medicaid also excludes some annuities from assets if they meet certain criteria. Annuities provide a way to maintain eligibility by offering a regular income, which is beneficial for maintaining financial security. The rules that govern this option must be understood and followed for successful implementation.
4. Paying Off Debt
Paying off debt is a direct method for asset preservation by reducing outstanding liabilities. Settlement of mortgages or other significant obligations minimizes the value of countable assets. This approach streamlines financials and provides greater peace of mind because debts are taken care of before applying to become eligible for assistance through Medicaid.
5. Home Improvements
This protects an asset while also enhancing its value. This is a possibility because Medicaid generally does not count the primary residence when considering assets. When individuals then upgrade or renovate their homes, they improve their lives and lessen their financial resources. Planning is essential to ensure that such responsible upgrades remain aligned with the individual’s objectives and planned strategies, thereby avoiding unnecessary expenditure.
6. Prepaying Funeral Expenses
A more pragmatic way is to pre-purchase your funeral and burial services. Individuals can use Medicaid to help save money for these future costs by establishing a special purpose fund, which can lower countable assets. A funeral trust or prepaid plan enables you to make essential arrangements for your funeral. This gives you peace of mind and frees up the financial capital for other uses.
7. Spousal Transfers
Married couples can reap the benefits by transferring their assets over to the spouse who does not apply for Medicaid. By doing so, the community spouse, or the spouse living at home, can retain more of the assets, which is a tactic known as spousal impoverishment protection. This option comes with rules and limits that are essential to be aware of if you want to maximize financial security while still meeting eligibility requirements.
8. Income-Producing Property
Having an income-generating asset can help contribute to asset protection. Correctly structured rental properties or income-generating investments may not count towards Medicaid’s asset values. This is then followed by a revenue stream that protects your resources. Expert help also helps you adhere to rules and maximize your financial benefits.
9. Creating a Life Estate
While one can solely own a piece of property, creating a life estate enables the owner to transfer the property while maintaining the right to live there for life. This option lowers the assets you can count, thereby preserving Medicaid eligibility. Your remainder interest passes to the beneficiaries you have named for future protection. This is executed with accurate documentation and legal advice.
10. Converting Assets to Income
An alternative option is converting assets to generate income. This could include purchasing annuities or investing in other income-generating assets. They potentially preserve Medicaid eligibility by converting capital into income in this fashion. Understanding the implications and rules behind this strategy is essential for its effective implementation.
Final Thoughts
A proper strategy and timing play a vital role in shielding the money before filing for Medicaid. Through means such as gifting, trusts, and other professional counsel, they can safeguard their resources and help maintain financial stability. These strategies help in preserving inheritance while establishing qualifying paths to long-term care for family members.

-

 Legal6 days ago
Legal6 days agoMichigan man JD Vance sentenced to 2 years for threatening Trump and JD Vance
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoU.S. to designate Maduro-linked Cartel de los Soles as terrorist organization
-
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoCambodia reports fatal H5N1 bird flu case in 22-year-old man
-

 World4 hours ago
World4 hours agoEthiopian volcano erupts for first time in thousands of years
-

 Legal4 days ago
Legal4 days agoWoman in critical condition after being set on fire on Chicago train
-
 World4 days ago
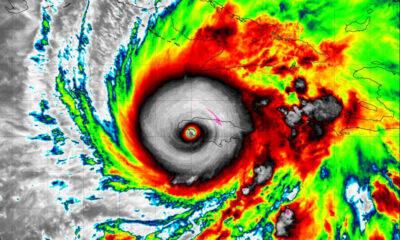
World4 days agoHurricane Melissa registered 252 mph wind gust, breaking global record
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoEpstein survivors release PSA calling on Congress to release all files
-

 Legal4 days ago
Legal4 days ago1 dead, 2 injured in shooting at Dallas Walmart parking lot



