US News
U.S. testing beef products for H5N1 bird flu
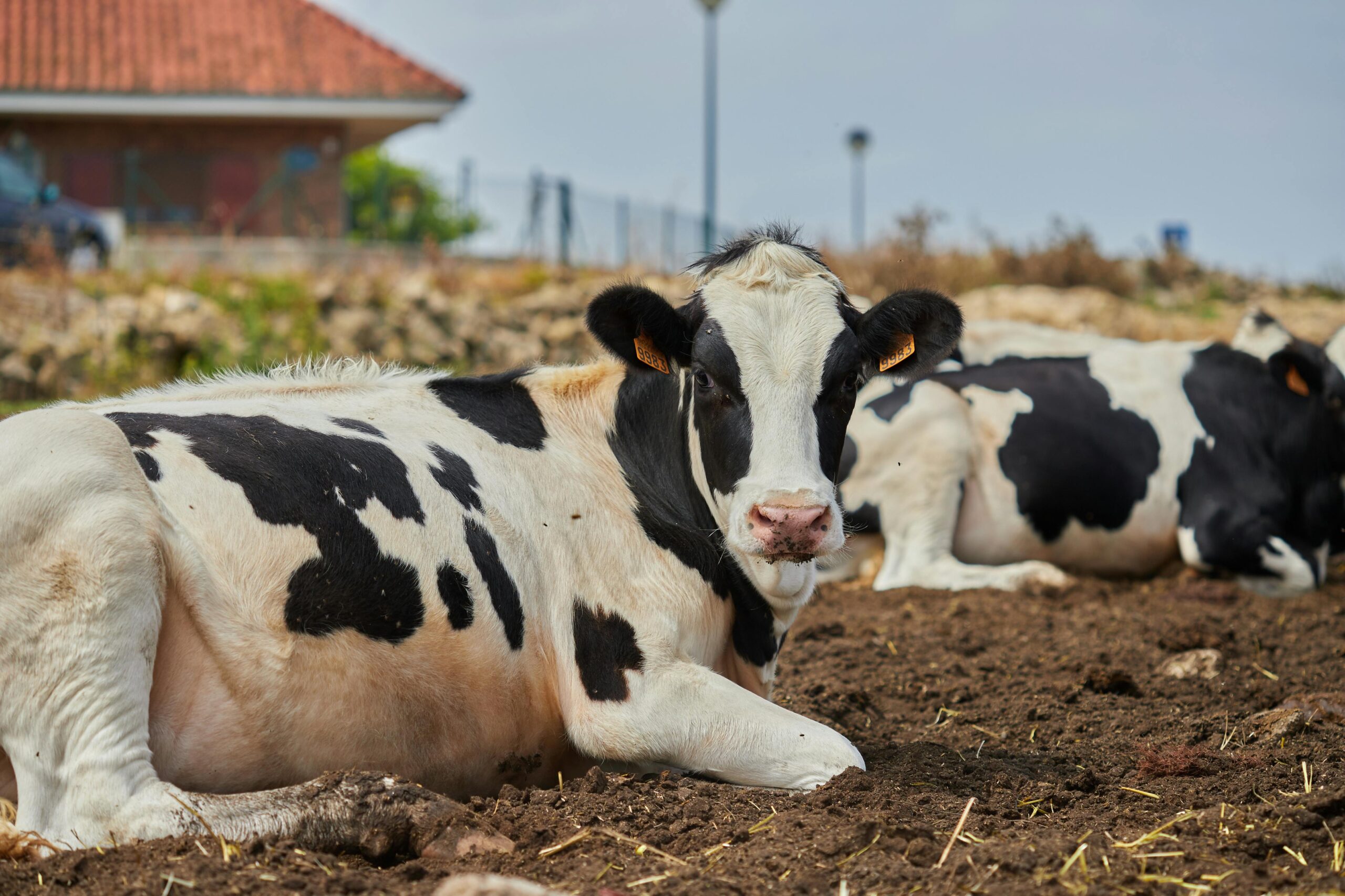

Ground beef being sold at retail stores in the U.S. is being tested for H5N1 bird flu, part of a wider investigation into an outbreak that’s affecting dairy cows, though officials remain confident that the meat is safe for human consumption.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) said it’s currently working on three separate beef safety studies to confirm that usual practices are sufficient to keep the meat supply safe from H5N1 bird flu.
“For the first, samples are being collected at retail outlets in the states in which dairy cow herds have tested positive for H5N1 influenza virus,” the spokesperson said. “The samples will be analyzed by APHIS using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which indicates whether any viral particles are present.”
For the second study, the Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) will visit slaughter facilities to collect muscle samples of cull dairy cattle condemned for systemic pathologies. Those samples will also be tested for H5N1.
“For both retail and at slaughter samples, any PCR positives will be evaluated for live virus by [the Agricultural Research Service (ARS)],” the spokesperson said.
Finally, the Agricultural Research Service will also conduct a beef cooking study, using a virus surrogate in ground beef and cooking it at different temperatures to determine log-reduction of the virus.
Although officials remain confident that the meat supply is safe, USDA is urging consumers to properly handle raw meat and cook it to a safe internal temperature, which kills bacteria and viruses.
The global spread of H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b – and the recent spread to a growing number of mammals – has raised concern about the possibility of a future variant which could lead to human-to-human transmission. So far, only a few human cases have been found after contact with infected birds or cattle.
USDA announced in late March that H5N1 had been found in unpasteurized milk from sick cows, making those the first-ever cases of bird flu in cattle. The number of outbreaks at dairy farms has since risen to 34 in 9 states and a farm worker in Texas also tested positive, along with 7 cats.
Last week, health officials confirmed that viral fragments of H5N1 bird flu had also been found in samples of commercial milk, but experts have said milk remains safe to drink because of pasteurization.
“The risk of avian influenza is evolving with the virus and needs real-time monitoring,” the World Health Organization said in a statement on Friday. “WHO and partners are asking countries to rapidly share information to enable this.”

-

 World6 days ago
World6 days agoEthiopian volcano erupts for first time in thousands of years
-

 Legal3 days ago
Legal3 days agoUtah Amber Alert: Jessika Francisco abducted by sex offender in Ogden
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoWoman in critical condition after being set on fire on Chicago train
-

 US News2 days ago
US News2 days agoExplosion destroys home in Oakland, Maine; at least 1 injured
-
 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHurricane Melissa registered 252 mph wind gust, breaking global record
-
 Health3 days ago
Health3 days agoMexico’s September human bird flu case confirmed as H5N2
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoSuspect in San Diego stabbing shot by authorities after fleeing into Mexico
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week ago1 dead, 2 injured in shooting at Dallas Walmart parking lot



