Reviews
Life-Saving Tech at Risk: How to Safeguard Medical Devices from Cyber Threats
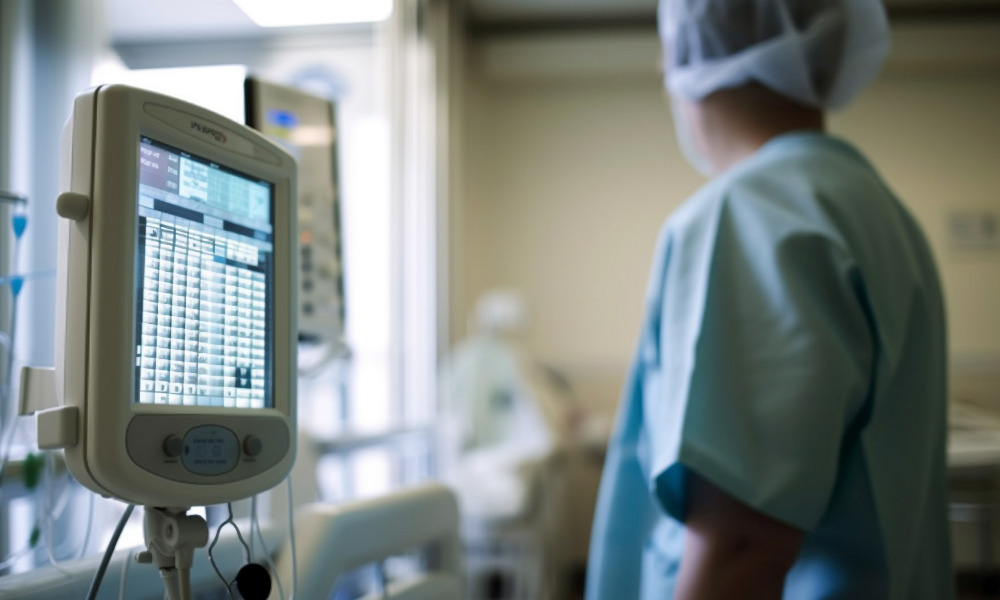
In today’s increasingly digital world, medical devices have become critical in saving lives and improving healthcare outcomes. From insulin pumps and pacemakers to connected imaging equipment, these devices rely heavily on technology to function effectively. However, as they become more sophisticated and interconnected, they become prime targets for cybercriminals. The question isn’t whether these devices can be hacked but how to prevent such incidents and protect the lives that depend on them.
Understanding the Importance of Medical Device Security
Medical devices are no longer standalone machines but integral parts of a connected healthcare ecosystem. They exchange data with hospital systems, electronic health records, and even smartphones, which enhances their efficiency. Yet, this connectivity comes with vulnerabilities. A successful cyberattack on a device could disrupt its operation, compromise sensitive patient data, or endanger lives in the worst cases. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is essential to maintaining trust in these life-saving technologies.
The Alarming Rise of Cyber Threats in Healthcare
The healthcare industry has seen a dramatic rise in cyberattacks over the past decade. Ransomware incidents, data breaches, and malware infections have plagued hospitals and medical facilities, creating ripple effects across the sector. Hackers often target medical devices because they are an entry point into larger networks. Once breached, these systems can lead to widespread chaos, affecting everything from patient records to essential equipment operations.
What Makes Medical Devices Vulnerable?
Due to their design priorities, medical devices often lag in cybersecurity. Developers focus on functionality, compliance, and patient safety, sometimes overlooking security. Additionally, many devices run on outdated operating systems that no longer receive patches or updates, leaving them vulnerable to new exploits. Limited processing power on some devices also restricts the implementation of robust security protocols.
The Role of Manufacturers in Device Security
Manufacturers are crucial in ensuring medical device cybersecurity. They must design products with security-by-design principles, integrating features like encryption, authentication mechanisms, and real-time monitoring. Regular firmware updates and clear guidance on secure usage can significantly reduce risks. Collaborative efforts between manufacturers, regulatory bodies, and healthcare organizations are key to creating a safer ecosystem.
Regulatory Measures to Protect Devices
Governments and regulatory agencies worldwide are stepping in to address the growing threat to medical devices. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued cybersecurity guidelines for device manufacturers, emphasizing the importance of risk assessment, vulnerability reporting, and post-market surveillance. Similar initiatives are being adopted globally, reflecting the urgency of safeguarding these technologies.
The Human Element: Training and Awareness
While technology is critical to cybersecurity, human behavior plays an equally significant role. Healthcare workers and administrators must be trained to recognize and respond to threats. Simple practices, such as avoiding suspicious emails, using strong passwords, and adhering to device usage protocols, can minimize risks.
Emerging Technologies to Combat Threats
Innovative solutions are being developed to strengthen medical device security. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms detect unusual activity and thwart cyberattacks in real time. Blockchain technology offers a secure framework for data exchange, ensuring integrity and transparency across healthcare systems. These advancements hold promise but require widespread adoption and integration.
How Healthcare Institutions Can Strengthen Security
Hospitals and clinics must adopt a proactive approach to protect their networks and devices. Conducting regular security audits, updating software, and investing in robust IT infrastructure are essential steps. Partnering with cybersecurity firms to simulate attacks and identify weaknesses can also be highly effective.
The Patient’s Role in Device Security
Patients using wearable medical devices or remote monitoring equipment must also be vigilant. Regularly updating device firmware, avoiding public Wi-Fi networks, and discussing cybersecurity concerns with healthcare providers can help mitigate risks. Empowering patients with knowledge is as critical as securing the devices themselves.
As the reliance on medical devices grows, so does the responsibility to protect them from cyber threats. Safeguarding these technologies is not just about protecting data but ensuring the health and safety of countless individuals who depend on them. Through a collaborative approach involving manufacturers, regulators, healthcare providers, and patients, the industry can build a robust defense against cyberattacks. Investing in security today will preserve trust and ensure the continued evolution of life-saving technology in the years to come.

-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoEthiopian volcano erupts for first time in thousands of years
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days ago8 kittens die of H5N1 bird flu in the Netherlands
-

 Legal7 days ago
Legal7 days agoUtah Amber Alert: Jessika Francisco abducted by sex offender in Ogden
-

 US News6 days ago
US News6 days agoExplosion destroys home in Oakland, Maine; at least 1 injured
-
 Health7 days ago
Health7 days agoMexico’s September human bird flu case confirmed as H5N2
-

 Legal3 days ago
Legal3 days ago15 people shot, 4 killed, at birthday party in Stockton, California
-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoWoman killed, man seriously injured in shark attack on Australia’s NSW coast
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoMarburg outbreak in Ethiopia rises to 12 cases and 8 deaths




