Reviews
Agnostic Cloud: Embracing Flexibility in the Cloud Computing World
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly looking for flexible and scalable solutions to meet their IT needs. One of the most talked-about innovations in this domain is the agnostic cloud. As companies strive to optimize their cloud environments, they are moving away from proprietary cloud platforms and adopting cloud-agnostic strategies. This article explores what an agnostic cloud is, its benefits, and why it is becoming an essential component of modern cloud infrastructure.
What is Agnostic Cloud?
An agnostic cloud refers to a cloud environment or service that is independent of any particular cloud provider. Essentially, it allows businesses to run their applications, workloads, and services on any cloud platform (such as AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or others) without being locked into one specific vendor. Cloud-agnostic solutions offer flexibility and portability, allowing organizations to move their workloads across different cloud platforms as needed, without rearchitecting their entire infrastructure.
This agnostic approach to cloud computing eliminates the need for businesses to commit exclusively to a single cloud provider, giving them the freedom to choose the best cloud service for their specific needs at any given time. As a result, businesses can avoid vendor lock-in and are better positioned to scale operations and optimize costs.
Key Benefits of Agnostic Cloud Solutions
1. Flexibility and Freedom of Choice
One of the main advantages of an agnostic cloud is the flexibility it offers. With an agnostic cloud model, businesses are not tied to the restrictions or limitations of a specific cloud provider. This freedom enables them to choose the cloud platform that best aligns with their business needs. For example, a company may choose to run its production workloads on AWS for scalability, while leveraging Google Cloud’s AI tools for data analytics.
2. Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in occurs when a business becomes overly dependent on a specific cloud provider’s services, making it difficult to switch providers without incurring significant costs or downtime. Cloud-agnostic solutions reduce this risk by allowing companies to maintain a level of independence. If a better or more cost-effective cloud platform emerges, businesses can migrate their workloads seamlessly, without being forced to stay with a single provider.
3. Cost Optimization
With an agnostic cloud, businesses can optimize their cloud expenses by choosing the most cost-effective solution for each workload. Providers offer different pricing models, so companies can take advantage of competitive pricing and choose the option that offers the best value for money. For example, some providers may offer cheaper storage, while others may provide better computing resources. By using multiple providers, organizations can ensure that they are not overpaying for any service.
4. Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Using an agnostic cloud approach increases redundancy and reliability. Organizations can distribute their workloads across multiple cloud providers, ensuring that if one provider experiences downtime or issues, the workloads can be shifted to another provider. This strategy helps maintain business continuity and ensures high availability, making it a valuable solution for mission-critical applications.
The Role of Cloud-Agnostic Tools
To make the most out of an agnostic cloud environment, businesses often turn to cloud-agnostic tools and platforms that facilitate the management and orchestration of their workloads. Tools like Kubernetes, Terraform, and containerization technologies provide a layer of abstraction that allows businesses to manage their cloud environments without being tied to a specific provider’s tools or services.
For instance, Kubernetes can be used to orchestrate containers across multiple cloud environments, ensuring consistency and portability. Similarly, Terraform enables infrastructure-as-code across multiple clouds, allowing businesses to provision resources seamlessly, regardless of the underlying cloud provider.
Challenges of Implementing an Agnostic Cloud
While the benefits of an agnostic cloud are clear, there are certain challenges to consider. One of the primary challenges is the complexity involved in managing multiple cloud environments. Integrating different cloud services, monitoring performance across various platforms, and ensuring data consistency can require sophisticated tools and expertise.
Additionally, not all cloud services are fully interoperable, which may lead to compatibility issues. Some cloud providers offer unique services that may not have direct equivalents on other platforms, making it difficult to fully migrate certain workloads without modifying the applications.
How to Move Toward an Agnostic Cloud Model
For businesses looking to move toward an agnostic cloud model, the first step is to assess their current infrastructure and identify which workloads could benefit from cloud agnosticism. This includes reviewing existing dependencies on specific cloud services and evaluating the potential for flexibility and scalability.
Next, businesses should invest in cloud-agnostic tools and technologies that enable seamless integration between different cloud providers. Ensuring that applications and infrastructure are designed with portability in mind will also help in making future migrations smoother.
Lastly, businesses should develop a strong cloud strategy that accounts for cost management, security, and disaster recovery. With the right planning, transitioning to an agnostic cloud model can deliver substantial long-term benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the agnostic cloud is a transformative concept in the cloud computing world, offering businesses the flexibility, cost efficiency, and scalability they need to stay competitive in the digital age. By adopting an agnostic cloud strategy, businesses can avoid vendor lock-in, optimize costs, and ensure greater reliability and flexibility in their cloud environments. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential benefits make the shift to an agnostic cloud an attractive option for businesses looking to future-proof their IT infrastructure.

-

 US News6 days ago
US News6 days agoJetBlue flight diverts to Tampa after altitude drop injures at least 15
-

 Breaking News14 hours ago
Breaking News14 hours agoAt least 3 dead, 11 injured after UPS cargo plane crashes near Louisville airport
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoU.S. Navy helicopter and fighter jet crash in South China Sea; all crew rescued
-
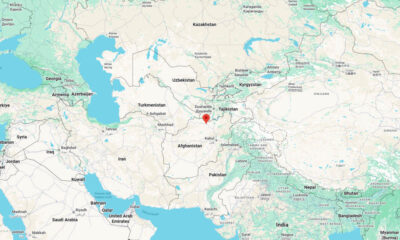
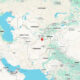 World3 days ago
World3 days agoStrong 6.3 earthquake strikes northern Afghanistan; felt across Pakistan
-

 World2 days ago
World2 days agoProtesters storm government building in Mexico after killing of local mayor
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days ago10 people stabbed on train in Huntingdon, England
-

 US News6 days ago
US News6 days agoTrump says U.S. will resume nuclear weapons testing ‘on an equal basis’
-

 US News1 week ago
US News1 week agoDamage reported in Kilgore, Texas following tornado warning




