Health
Texas woman died from brain-eating amoeba after using RV tap water for nasal rinse
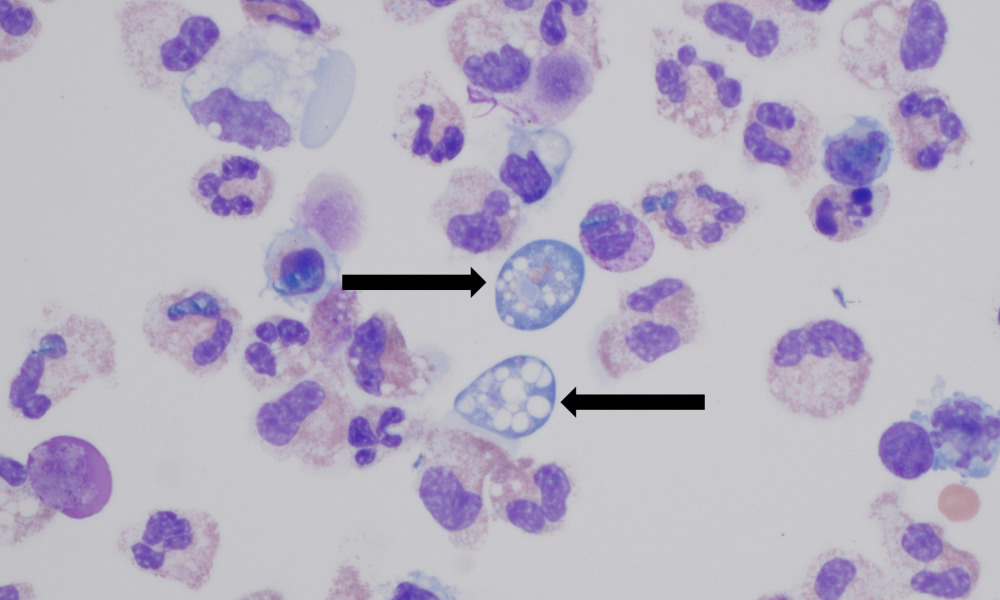
A 71-year-old Texas woman died after contracting a rare and deadly brain infection caused by Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the “brain-eating amoeba,” after using tap water from a recreational vehicle (RV) for nasal irrigation, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The woman developed symptoms of primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) in 2024, including fever, headache, and altered mental status, four days after using an over-the-counter nasal rinse bottle filled with unboiled tap water from her RV while staying at a campground.
She later suffered seizures and died eight days after the onset of symptoms. Laboratory testing confirmed the presence of N. fowleri in her cerebrospinal fluid.
The CDC report states the woman had no recent exposure to lakes or rivers, where the amoeba is typically found. Instead, she had used water from her RV’s plumbing system, which was connected at the time to the campground’s municipal water supply via a hose and external filter. The RV also contained an onboard storage tank that had been filled at an unknown date before the woman purchased the vehicle three months earlier.
An investigation by the CDC and the Texas Department of State Health Services did not detect N. fowleri in any of the 12 environmental samples collected from the RV or the campsite’s water system. However, tests revealed water quality problems.
Disinfectant levels at the municipal connection were far below state standards, and water turbidity—an indicator of cloudiness—was significantly higher than recommended for drinking water. These conditions suggest a breakdown in disinfection that may have allowed harmful organisms to grow in biofilms, which can shield pathogens like N. fowleri.
Officials say the time lapse between water use and sample collection—23 days—may explain why the amoeba was not found. It’s possible that environmental conditions had changed or that the organism was present but at levels below detection limits.
Because both the RV’s tank and the municipal water supply were in use at different times, investigators could not determine which was the source of the contamination.
The CDC emphasized that tap water should never be used for nasal rinsing unless it has been distilled, sterilized, or boiled and cooled beforehand. Drinking water that meets safety standards may still contain small amounts of microorganisms that are safe to ingest but dangerous if introduced through the nasal passages.
Although infections from Naegleria fowleri are extremely rare in the U.S., they are almost always fatal.

-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoEthiopian volcano erupts for first time in thousands of years
-

 Legal4 days ago
Legal4 days agoUtah Amber Alert: Jessika Francisco abducted by sex offender in Ogden
-

 US News3 days ago
US News3 days agoExplosion destroys home in Oakland, Maine; at least 1 injured
-
 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoMexico’s September human bird flu case confirmed as H5N2
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoSuspect in San Diego stabbing shot by authorities after fleeing into Mexico
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoMarburg virus outbreak in Ethiopia grows to 6 confirmed cases
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoWoman killed, man seriously injured in shark attack on Australia’s NSW coast
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoU.S. sanctions companies and vessels accused of aiding Iranian military oil sales




