Reviews
GHK Basic Peptide: Cellular and Systemic Processes

The Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine (GHK) peptide, also known as GHK Basic, is a naturally occurring tripeptide consisting of the amino acids glycine, histidine, and lysine. This peptide has attracted considerable scientific interest due to its diverse potential. GHK Basic’s unique structural features and interactions with various molecular targets suggest that it may influence a range of cellular and systemic processes.
GHK Basic: Structural Features and Molecular Interactions
GHK Basic is distinguished by its specific amino acid sequence, which is believed to enable it to engage in complex biochemical interactions. One of the peptide’s notable properties is its potential to chelate metal ions, particularly copper. Copper chelation is believed to influence several enzymatic processes. This interaction might modulate the activity of metalloenzymes. Metalloenzymes are essential for numerous biochemical reactions, including those involved in cellular repair and oxidative stress responses.
Additionally, the peptide has been hypothesized to interact with specific cellular receptors, potentially impacting signal transduction pathways. It has been theorized that GHK Basic may bind to cell surface receptors, which may trigger intracellular signaling cascades that may influence gene expression. These pathways are thought to be critical for regulating various cellular functions, such as proliferation, differentiation, and migration.
GHK Basic: Cellular Processes
One of the most compelling areas of interest surrounding GHK Basic is its hypothetical role in cellular repair and regeneration. The peptide’s impact on extracellular matrix (ECM) synthesis is particularly noteworthy to researchers. ECM components like collagen and glycosaminoglycans are thought to play a crucial role in maintaining tissue integrity and facilitating repair processes. Studies suggest that GHK Basic may stimulate the production of these components, which might contribute to the reconstruction of damaged tissue architecture.
In addition to its possible role in ECM synthesis, GHK Basic is hypothesized to influence the inflammatory response. Inflammation is believed to be a critical component of the healing process, but excessive or prolonged inflammation may impair tissue repair. Research indicates that GHK Basic might modulate the activity of various cytokines and growth factors involved in inflammation. This may help balance an inflammatory response and create an environment conducive to healing.
GHK Basic: Oxidative Stress
The potential antioxidant properties of GHK Basic add another dimension to its activity. The peptide’s potential to chelate metal ions may reduce the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are hypothesized to contribute to oxidative stress and cellular damage. By mitigating oxidative damage, GHK Basic may help preserve cellular integrity and function.
The peptide’s possible impact on oxidative stress is believed to be particularly relevant in the context of cellular aging. Over time, the accumulation of oxidative damage is thought to contribute to cellular dysfunction and tissue degeneration. Investigations purport that GHK Basic might play a role in mitigating these impacts by enhancing the organism’s potential to cope with oxidative stress. Its potential to support the maintenance of extracellular matrix components, such as collagen, further underscores its relevance in addressing age-related changes in tissue structure and function.
GHK Basic: Immunity
The possible impact of GHK Basic on the immune system is an area of growing interest to researchers. It has been proposed that the peptide might modulate the activity of various immune cells, including macrophages and lymphocytes. This modulation might influence the organism’s immune response, which may enhance its potential to respond to infections and resolve inflammation.
Findings imply that GHK Basic might also influence the production of antimicrobial peptides, which are thought to be integral to the innate immune response. By promoting the synthesis of these peptides, GHK Basic may potentially bolster the organism’s defense mechanisms against microbial pathogens. This hypothetical immunomodulatory impact highlights the peptide’s potential role in supporting overall immune function.
GHK Basic: Neurobiology
Recent research has expanded the scope of GHK Basic to include potential neuroprotective properties. The peptide is theorized to influence the expression of genes involved in neuronal function. This includes the potential upregulation of neurotrophic factors, which are believed to be crucial for the survival, growth, and maintenance of neurons.
Additionally, GHK Basic appears to impact synaptic plasticity, a fundamental process thought to support learning and memory. Synaptic plasticity involves changes in the strength and efficiency of synaptic connections, which are thought to be essential for cognitive processes. By modulating the expression of proteins associated with synaptic function, GHK Basic may potentially support cognitive function and neural resilience.
GHK Basic: Implications for Regenerative Contexts
Given its diverse impacts, GHK Basic is thought to hold promise in the field of regenerative studies. Researchers have explored its potential to enhance tissue repair, modulate inflammation, and support extracellular matrix synthesis. Some researchers have expressed their opinion that GHK Basic may be valuable in developing approaches to tissue damage and degeneration. The peptide’s potential seems to be promising in some studies related to wound healing to degenerative diseases.
Research into GHK Basic’s impact on cellular and systemic processes may also lead to novel approaches in biotechnology. For instance, there may be potential for its properties to be harnessed to create advanced biomaterials or research agents designed to promote tissue regeneration and repair. As understanding of the peptide’s mechanisms of action deepens, it may pave the way for innovative studies in regenerative and experimental contexts.
GHK Basic: Future Research Directions
The current understanding some researchers have of GHK Basic is based on a combination of theoretical insights and experimental speculation. However, further research is needed to fully elucidate the peptide’s mechanisms of action and full range of potential. Future investigations might focus on detailed studies of GHK Basic’s interactions with cellular receptors, its hypothetical impact on specific signaling pathways, and its proposed role in various physiological processes.
Additionally, exploring the peptide’s impacts in different biological contexts and laboratory models could provide valuable insights into its potential applications. Long-term studies and experimental investigations will be crucial in determining the full extent of GHK Basic’s impacts and its suitability for various research studies.
GHK Basic: Conclusion
GHK Basic peptide is considered among researchers to be a molecule of considerable scientific and research interest. This is partially due to its multifaceted impacts on cellular and systemic processes. From its alleged role in cellular repair and regeneration to its potential antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective properties, the peptide’s diverse activities reflect its complex biochemical interactions.
As research continues to explore the peptide’s mechanisms of action, GHK Basic may offer new avenues for addressing various challenges. The ongoing exploration of GHK Basic underscores the significance of peptides in regulating biological systems and highlights their potential for advancing biotechnology. Researchers looking for peptides made in the USA are encouraged to visit Biotech Peptides.
References
[i] Pickart L, Margolina A. Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide in the Light of the New Gene Data. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 7;19(7):1987. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071987. PMID: 29986520; PMCID: PMC6073405.
[ii] Dymek M, Olechowska K, Hąc-Wydro K, Sikora E. Liposomes as Carriers of GHK-Cu Tripeptide for Cosmetic Application. Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 18;15(10):2485. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102485. PMID: 37896245; PMCID: PMC10610410.
[iii] Rosenfeld M, Nickel K, Ladiges W. GHK peptide prevents sleep-deprived learning impairment in aging mice. Aging Pathobiol Ther. 2023;5(1):33-35. doi: 10.31491/apt.2023.03.109. Epub 2023 Mar 29. PMID: 37035833; PMCID: PMC10081520.
[iv] Wang X, Liu B, Xu Q, Sun H, Shi M, Wang D, Guo M, Yu J, Zhao C, Feng B. GHK-Cu-liposomes accelerate scald wound healing in mice by promoting cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Wound Repair Regen. 2017 Apr;25(2):270-278. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12520. Epub 2017 Apr 27. PMID: 28370978.
[v] Dou Y, Lee A, Zhu L, Morton J, Ladiges W. The potential of GHK as an anti-aging peptide. Aging Pathobiol Ther. 2020 Mar 27;2(1):58-61. doi: 10.31491/apt.2020.03.014. PMID: 35083444; PMCID: PMC8789089.
This is a contributed article, its content does not necessarily represent the views of BNO News.

-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoEthiopian volcano erupts for first time in thousands of years
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoMichigan man JD Vance sentenced to 2 years for threatening Trump and JD Vance
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoWoman in critical condition after being set on fire on Chicago train
-
 World1 week ago
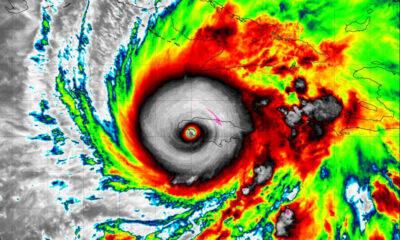
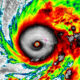
World1 week agoHurricane Melissa registered 252 mph wind gust, breaking global record
-

 Legal6 days ago
Legal6 days agoSuspect in San Diego stabbing shot by authorities after fleeing into Mexico
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week ago1 dead, 2 injured in shooting at Dallas Walmart parking lot
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoMarburg virus outbreak in Ethiopia grows to 6 confirmed cases
-

 Legal4 hours ago
Legal4 hours agoUtah Amber Alert: Jessika Francisco abducted by sex offender in Ogden