Reviews
Museum Shelving: 12 Techniques to Preserve History Safely
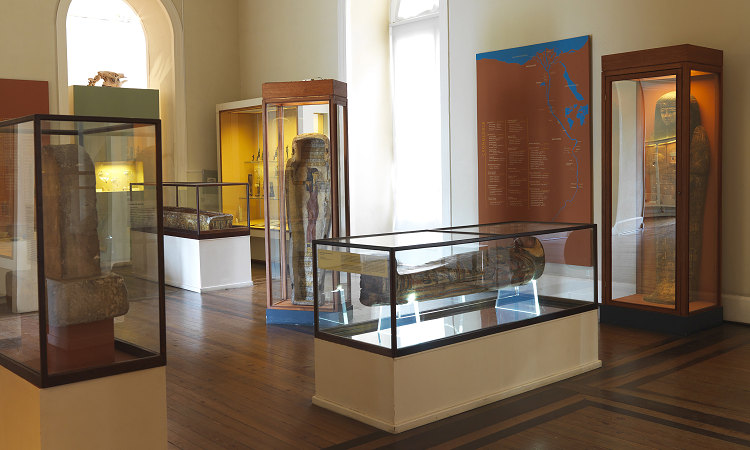

Preserving history requires a delicate balance between accessibility and security. Museum shelving plays a crucial role in organizing and storing valuable artifacts, documents, and objects for future generations. In this article, we will explore twelve techniques that museums employ to safely preserve historical materials.
1. Aesthetics Meets Functionality: Customized Shelving Solutions
When it comes to a museum shelving system, aesthetics should not take precedence over functionality. Customized shelving solutions help maximize available space while accommodating various artifact sizes, shapes, and weights. By using adjustable shelves, museums can adapt their storage requirements as collections evolve over time.
2. Conservation-Friendly Materials: Say No to Harmful Chemicals
Using conservation-friendly materials for museum shelving is essential for preventing any deterioration or damage to historical items. Avoiding harsh chemicals and opting for non-reactive materials such as inert metals or low-acidity solid woods helps preserve artifacts in their original condition.
3. Climate Control: The Key to Consistent Preservation
Maintaining stable environmental conditions is vital for preserving fragile objects in museums. Effective climate control systems regulate temperature, humidity levels, and air quality within an acceptable range, preventing deterioration caused by fluctuations.
4. Light Control: Shielding Artifacts from Harmful UV Radiation
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause irreversible damage to artifacts by fading colors and causing structural degradation. To protect sensitive materials like textiles and photographs from harmful light exposure, museum shelving often includes UV filtering options like tempered glass or acrylic display covers.
5. Secure Enclosures: Keeping Valuables Safe from Risks
Museum storage areas require secure enclosures with limited access points to ensure strict control over who can handle valuable items. Implementing lockable cabinets or compartmentalized secured spaces guarantees the safety of historically significant collections.
6. Divides Are Good: Compartmentalization for Artifact Segregation
Dividing shelves and creating distinct storage compartments allow museums to group artifacts according to their material type, size, or sensitivity. This organization not only improves accessibility but also prevents any cross-contamination or accidental damage caused by contact with incompatible materials.
7. Padded Protection: Safeguards against Accidental Bumps
Museum shelving can include padded inserts and linings to provide a cushioning effect for fragile objects. This helps protect delicate items from accidental bumps, reducing the chances of surface damage.
8. Proper Labeling: Enhancing Inventory Management
Accurate inventory management is critical for efficient artifact retrieval and tracking. Museum shelving should allow for clear labeling on shelves, drawers, and boxes so that collections remain well-organized and easily identifiable.
9. Efficient Space Utilization: Compact Storage Solutions
Museums often need to store a significant number of items within limited space constraints. Compact storage solutions like high-density mobile shelving systems maximize space utilization by allowing aisles to be opened as needed while keeping artifacts protected when not accessed.
10. Handling Made Easy: Pull-Out Shelves or Sliding Trays
Pull-out shelves or sliding trays facilitate safer handling of artifacts during the retrieval process. By providing easy access without putting strain on delicate objects, these features minimize the risk of accidental damage during the handling process.
11. Regular Inspections: Preventive Measures in Action
Implementing a regular inspection routine ensures that any signs of deterioration or pest activity are detected early on. Well-designed museum shelving should allow easy inspections without interrupting the storage area’s integrity or disturbing nearby items.
12. Fire Safety Standards: Protecting Priceless Treasures
Preserving history means safeguarding artifacts from potential threats such as fire accidents. Museum shelving should comply with rigorous fire safety standards by using flame-resistant materials and facilitating an efficient firefighting response system within storage areas.
Conclusion
The techniques mentioned above highlight various aspects involved in safely preserving historical treasures through the effective use of museum shelving. By implementing appropriate storage solutions, museums can maintain the integrity and accessibility of their collections for generations to come. Ensuring conservation-friendly materials, climate control, secure enclosures, compartmentalization, and efficient space utilization are just a few ways museums preserve history safely. Adopting these techniques allows not only accurate inventory management but also protects artifacts from potential damage caused by light exposure, handling errors, or environmental factors.

-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoEthiopian volcano erupts for first time in thousands of years
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoMichigan man JD Vance sentenced to 2 years for threatening Trump and JD Vance
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week agoWoman in critical condition after being set on fire on Chicago train
-
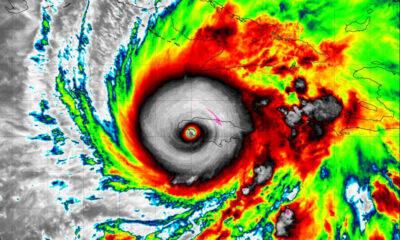
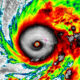 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHurricane Melissa registered 252 mph wind gust, breaking global record
-

 Legal6 days ago
Legal6 days agoSuspect in San Diego stabbing shot by authorities after fleeing into Mexico
-

 Legal1 week ago
Legal1 week ago1 dead, 2 injured in shooting at Dallas Walmart parking lot
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoMarburg virus outbreak in Ethiopia grows to 6 confirmed cases
-

 Legal5 hours ago
Legal5 hours agoUtah Amber Alert: Jessika Francisco abducted by sex offender in Ogden