Reviews
Comparison: Natural Colored Diamonds vs Enhanced Diamonds

Deep beneath Earth’s surface, extreme pressure and heat occasionally produce nature’s rare gems: colored diamonds. Though most people think of diamonds as colorless, these rare gems—known as fancy colored diamonds—derive their distinctive hues from trace elements or structural variations in their carbon structure. Unlike conventional natural diamonds for sale that jewelers prize for their absence of color, these extraordinary gems display a spectrum from subtle champagnes to vivid yellows, pinks, blues, and the exceedingly rare reds.
Natural Colored Diamonds: Nature’s Rare Masterpieces
Natural colored diamonds form over billions of years under extreme conditions deep within Earth’s mantle. Their colors develop through several mechanisms:
- Atomic substitution: When foreign elements replace carbon atoms (nitrogen creates yellow hues, boron produces blue diamonds)
- Structural defects: Pink and red diamonds form through plastic deformation during ascent
- Natural irradiation: Green diamonds develop when radiation displaces carbon atoms
Natural colored diamonds are extremely rare. Only about one in 10,000 gem-quality diamonds has natural color, and stones with intense color are even scarcer. Red diamonds are so rare that only about 30 true red diamonds over 0.20 carats exist worldwide, while blue diamonds constitute less than 0.1% of all colored diamonds.
This extreme scarcity drives exceptional value. The Pink Star, a 59.60-carat fancy vivid pink diamond, sold for $71.2 million in 2017, while fancy vivid blue specimens can command over $1 million per carat. The GIA classifies these stones based on hue (dominant color), saturation (intensity from faint to fancy vivid), and tone (lightness or darkness). The difference between intensity grades dramatically impacts value – a fancy vivid blue diamond may command 3-5 times the price of a fancy blue of the same carat weight.
From an investment perspective, natural colored diamonds have appreciated approximately 77% between 2010-2020 according to Knight Frank’s Luxury Investment Index. Unlike colorless diamonds, which typically lose 20-40% of retail value immediately after purchase, exceptional colored diamonds often retain and increase in value.
Enhanced Colored Diamonds: Technology Meets Gemology
Modern gemological science has revolutionized the diamond industry by developing sophisticated techniques to create colored diamonds through laboratory enhancement. These processes include:
HPHT Treatment subjects diamonds to temperatures exceeding 2000°C and pressure above 60,000 atmospheres, transforming brown diamonds into colorless, yellow, orange, pink, blue, or green specimens by altering atomic arrangements. These treatments are permanent and stable.
Irradiation and Annealing expose diamonds to radiation followed by controlled heating, creating blue, green, pink or red stones depending on the specific techniques used. Some irradiated colors may fade if exposed to prolonged heat or intense sunlight.
Coating Methods apply thin layers of colored material to a diamond’s surface. These treatments are less permanent than other methods and may require special care to maintain their appearance.
Identifying enhanced diamonds requires specialized equipment and expertise. Under microscopic examination, enhanced diamonds show distinctive features:
- HPHT-treated stones display characteristic graphitization around inclusions
- Irradiated diamonds show concentrated color at facet junctions
- Coated diamonds reveal unusual surface features when viewed with immersion microscopy
The price differential between natural and enhanced colored diamonds is substantial. While a natural fancy vivid blue diamond may command $500,000-$1,000,000 per carat, a similar-looking HPHT-treated blue diamond might sell for $5,000-$10,000 per carat—roughly 1-2% of the natural stone’s value.
Synthetic vs. Enhanced: Important Distinctions
It’s crucial to distinguish between enhanced diamonds and synthetic (lab-grown) diamonds. Enhanced diamonds begin as natural diamonds that undergo treatments to modify their color. Synthetic diamonds are created entirely in laboratory settings through processes that replicate natural diamond formation. While both offer alternatives to natural colored diamonds, they represent different categories with different value propositions and market positions.
Making an Informed Choice: Factors to Consider
When deciding between natural and enhanced colored diamonds, several critical factors should guide your decision:
Certification is essential. A report from a respected laboratory like GIA, IGI, or HRD provides crucial authentication of a diamond’s characteristics. For natural colored diamonds, look for “natural color” or “natural origin” on the certificate. Enhanced diamonds will be clearly marked with terms like “treated,” “irradiated,” or “HPHT processed.”
Value considerations differ dramatically. Natural colored diamonds represent potential investment assets with appreciation potential, while enhanced diamonds should be viewed primarily as decorative purchases with minimal resale value.
Durability and maintenance vary by treatment type. While natural and HPHT-treated diamonds require standard care, irradiated stones should avoid prolonged heat exposure, and coated diamonds need protection from abrasive materials and some chemicals.
Ethical considerations have become increasingly important. Natural colored diamonds should have proper Kimberley Process certification, while some enhanced diamonds repurpose lower-quality stones that might otherwise go unused.
Personal preferences and budget often determine the final decision:
- For investment potential, natural colored diamonds are superior (budget permitting)
- For specific colors at accessible price points, enhanced diamonds offer remarkable value
- For larger stones with vibrant color, enhancement technologies provide otherwise unattainable options
Expert tip: Request specific care instructions when purchasing an enhanced diamond, as some treatments may require special maintenance to preserve their appearance over time.
Both natural and enhanced colored diamonds have legitimate places in the market. Natural colored diamonds represent geological rarities with exceptional beauty and investment potential. Enhanced colored diamonds showcase technological achievement, democratizing access to colored diamonds for more consumers.
The key to satisfaction lies not in which category you choose, but in making your choice with complete information and appropriate expectations. In the diverse spectrum of colored diamonds, knowledge remains the most valuable asset of all.

-

 US News6 days ago
US News6 days agoUnwarned tornado suspected in Fort Worth as storms cause damage and power outages
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoU.S. Navy helicopter and fighter jet crash in South China Sea; all crew rescued
-

 Legal5 days ago
Legal5 days agoMultiple injured in shooting at Lincoln University in Pennsylvania
-
 World1 week ago
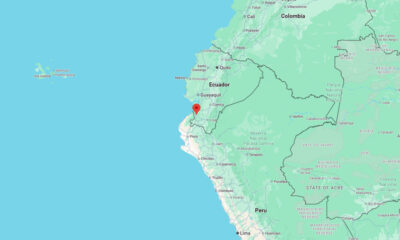
World1 week agoMagnitude 6.1 earthquake strikes Ecuador–Peru border region
-
 World1 week ago
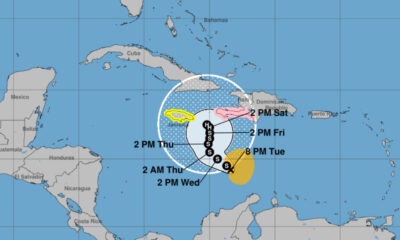
World1 week agoHurricane watch issued for Haiti due to Tropical Storm Melissa
-

 US News2 days ago
US News2 days agoDamage reported in Kilgore, Texas following tornado warning
-

 US News21 hours ago
US News21 hours agoTrump says U.S. will resume nuclear weapons testing ‘on an equal basis’
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRare tornado in northern France kills 1 and injures 9



