Reviews
How Does Globalization Affect AML Legislation?
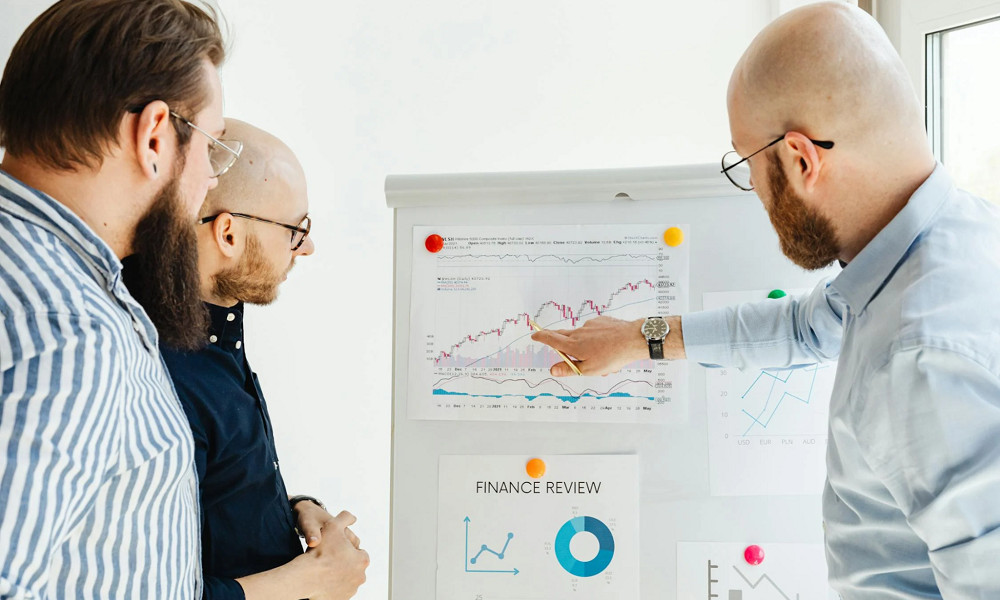

Globalization has changed the functioning of businesses and financial markets in an unprecedented manner. It has, however, posed challenges, particularly in terms of financial crime prevention. At the center of Globalization is the concept of Anti Money Laundering (AML) legislation, which has greatly changed. If interested, you can get a certification and learn more at amlcertification.com.
Overall, money laundering and other financial crimes tend to be more transnational than ever before, an entire global effort seems to be in more need than ever before too.
Financial Crimes Globalization
Over the last few decades, globalization has sought to ‘connect’ the world or bring that world closer. Networks and flow of information has invariably become easier. This has led to exploitable financial systems or criminals garnering opportunities.
Money laundering, terrorism financing, and other activities from nefarious and illegal organizations are not activities done at a single location; rather, it is the whole out the outsourcing of devious minds ensuring that these tasks are carried out invisibly.
International Cooperation and Regulatory Frameworks
Cooperation has become one of the critical elements in combating money laundering as financial crimes start to occur in several nations.
The goal of regulating and implementing anti money laundering laws is facilitated by a number of international bodies including the Financial Action Task Force, which helps to formulate and implement anti money laundering laws worldwide. FATF, created in 1989, issues international benchmarks concerning policies aimed at combating money laundering and advises member states to endorse the established standards in their legislation.
The FATF’s recommendations encompass a wide variety of areas, such as identifying and verifying clients, maintaining certain records, and reporting suspicious activity. The FATF helps internationalize the standards that countries are increasingly required to adopt to prevent financial and other crimes, such as money laundering, in their territories. This coordination reduces the chances of exploiting loopholes and makes sure that criminals are unable to just shift their dirty money to nations with weaker AML laws.
Challenges Posed by Globalization to AML Legislation
As much as globalization has nurtured the processes of international collaboration and the formation of global frameworks in the fight against money laundering, it has also posed a number of problems, such as:
- Inequalities in the Country Level: Nation-states have different degrees of existence, applicability, and enforcement of doctrines and legal measures against money laundering.
While some countries have gone to the extent of formulating laws and regulations, others may not have strict laws, or their enforcement may be inadequate, providing criminals with a chance to take advantage of countries that are less stringent. This situation may impede the efforts aimed at preventing money laundering at the international level.
- Cross-Border Flow of Transactions: With more and more transactions occurring across the globe so would be the difficulty for authorities in tracking the transactions and how money is moving.
Criminals are able to network for funds through a combination of national regulations and movement of funds across countries undetected making it difficult for authorities to trace criminal funds.
- Emerging Technology and Financial Developments: Such emergence as the popularity of cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology outrunning expansion, and delivery of online financial services have introduced additional complexities in the AML framework.
Those technologies can be leveraged to complete transactions in an anonymous manner, which makes it difficult for enforcement authorities to supervise and control illicit activities. Financial institutions have to embrace these changes as well and revisit their anti-money laundering measures accordingly.
- Geographic Factor and Politics: Global AML measures are frequently affected by the territorialism of cultures, politics, and economies of different countries. If in some countries the enforcement of AML stands as a non issue, in other countries political factors render it to be a non enforcement issue.
Globalization and AML Compliance
As much as globalization is taking center stage in the world’s economy, it will also have effects on the stricter AML compliance that will be necessary in the future.
For the problems discussed above, the most appropriate response seems to be international dialogue; cooperation between world organizations and national regulators, as of late, has helped create and increase the cohesiveness and effectiveness of anti-money laundering programs. There are plans to foster understanding between nations, facilitate the procedures of compliance, and focus on the use of newer sources of finance without detracting from AML procedures.
In addition to this, there is also a growing focus on both the private sector’s and multilateral organizations’ strategic role in the fight against financial crime. The most important challenge is for banks, non-banking financial organizations, technology companies, and policymakers to work together and develop tools that will help to control non-compliant actions at the point of service. Strategic data utilization and more AI tools will become the name of the game in the near future.
What to Expect?
The world economy is integrated, which has given rise to new types of financial illicit activities that are harder to combat. Indeed, it has resulted in ameliorated international frameworks, collaborative efforts, and uniform regulations, which make it easy for the world to respond to financial malpractices.
As globalization is set to continue, so must the AML legislation so that the financial apparatus does not remain too lapsed in the risk posed by facing international crime.

-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoEthiopian volcano erupts for first time in thousands of years
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days ago8 kittens die of H5N1 bird flu in the Netherlands
-

 Legal7 days ago
Legal7 days agoUtah Amber Alert: Jessika Francisco abducted by sex offender in Ogden
-

 US News6 days ago
US News6 days agoExplosion destroys home in Oakland, Maine; at least 1 injured
-
 Health7 days ago
Health7 days agoMexico’s September human bird flu case confirmed as H5N2
-

 Legal3 days ago
Legal3 days ago15 people shot, 4 killed, at birthday party in Stockton, California
-

 World7 days ago
World7 days agoWoman killed, man seriously injured in shark attack on Australia’s NSW coast
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoMarburg outbreak in Ethiopia rises to 12 cases and 8 deaths




